Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 29 maio 2024
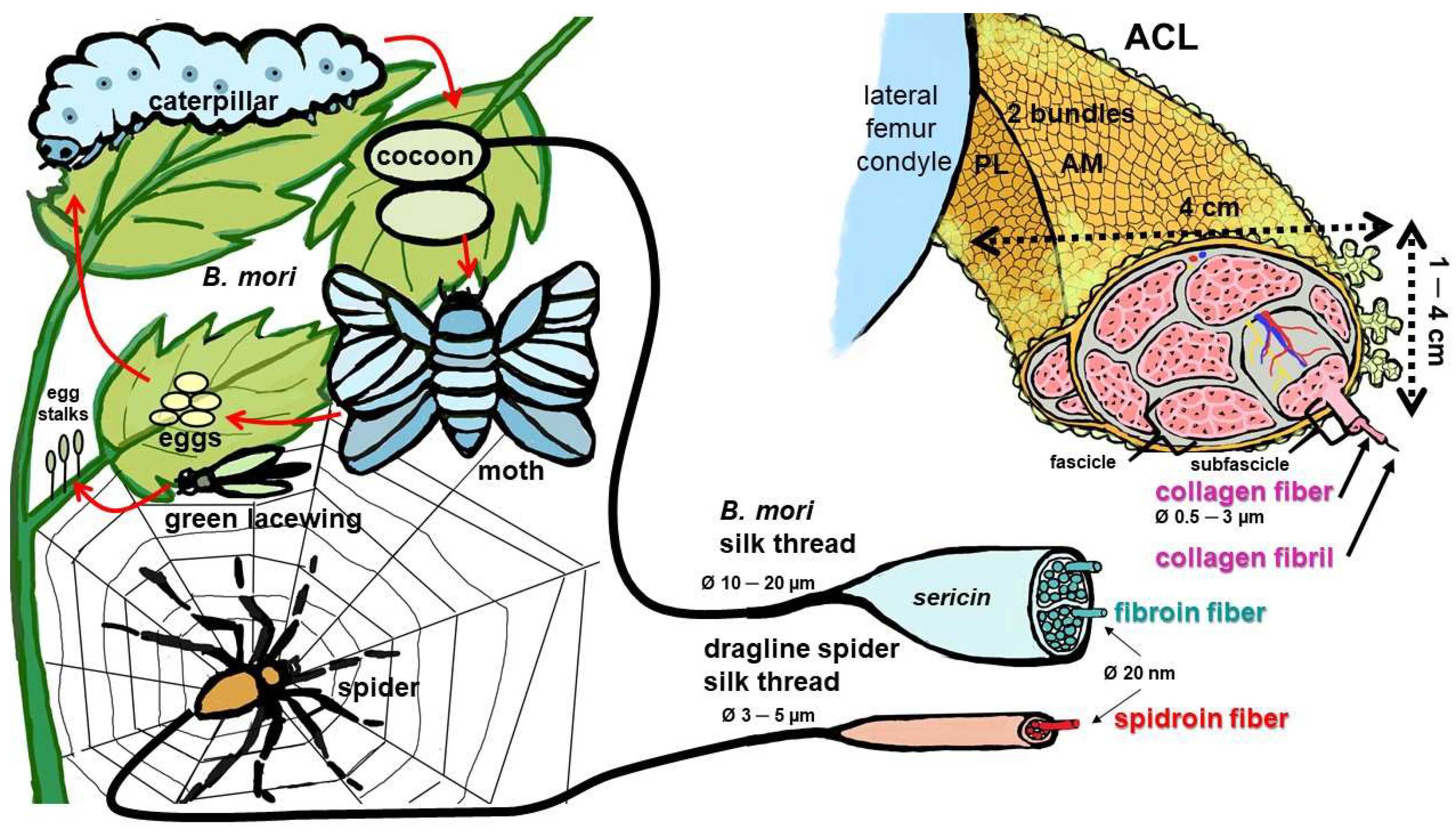
Silk has a long history as an exclusive textile, but also as a suture thread in medicine; nowadays, diverse cell carriers are manufactured from silk. Its advantages are manifold, including high biocompatibility, biomechanical strength and processability (approved for nearly all manufacturing techniques). Silk’s limitations, such as scarcity and batch to batch variations, are overcome by gene technology, which allows for the upscaled production of recombinant “designed” silk proteins. For processing thin fibroin filaments, the sericin component is generally removed (degumming). In contrast to many synthetic biomaterials, fibroin allows for superior cell adherence and growth. In addition, silk grafts demonstrate superior mechanical performance and long-term stability, making them attractive for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tissue engineering. Looking at these promising properties, this review focusses on the responses of cell types to silk variants, as well as their biomechanical properties, which are relevant for ACL tissue engineering. Meanwhile, sericin has also attracted increasing interest and has been proposed as a bioactive biomaterial with antimicrobial properties. But so far, fibroin was exclusively used for experimental ACL tissue engineering approaches, and fibroin from spider silk also seems not to have been applied. To improve the bone integration of ACL grafts, silk scaffolds with osteogenic functionalization, silk-based tunnel fillers and interference screws have been developed. Nevertheless, signaling pathways stimulated by silk components remain barely elucidated, but need to be considered during the development of optimized silk cell carriers for ACL tissue engineering.

Harnessing Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Therapy - Gowing Life
An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.

Challenging Post-translational Modifications in the Cell-free Protein Synthesis System - Synthetic Biology and Engineering - Full-Text HTML - SCIEPublish
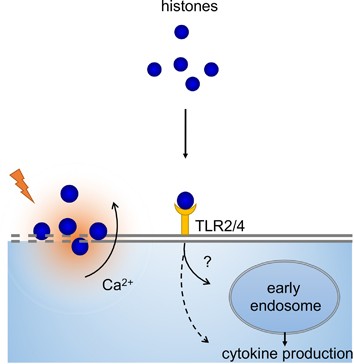
Extracellular histones, cell-free DNA, or nucleosomes: differences in immunostimulation
THE LIVES OF A CELL : LEWIS THOMAS : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive

Effect of calendar ageing on the cycle life of anode-free full-cells.
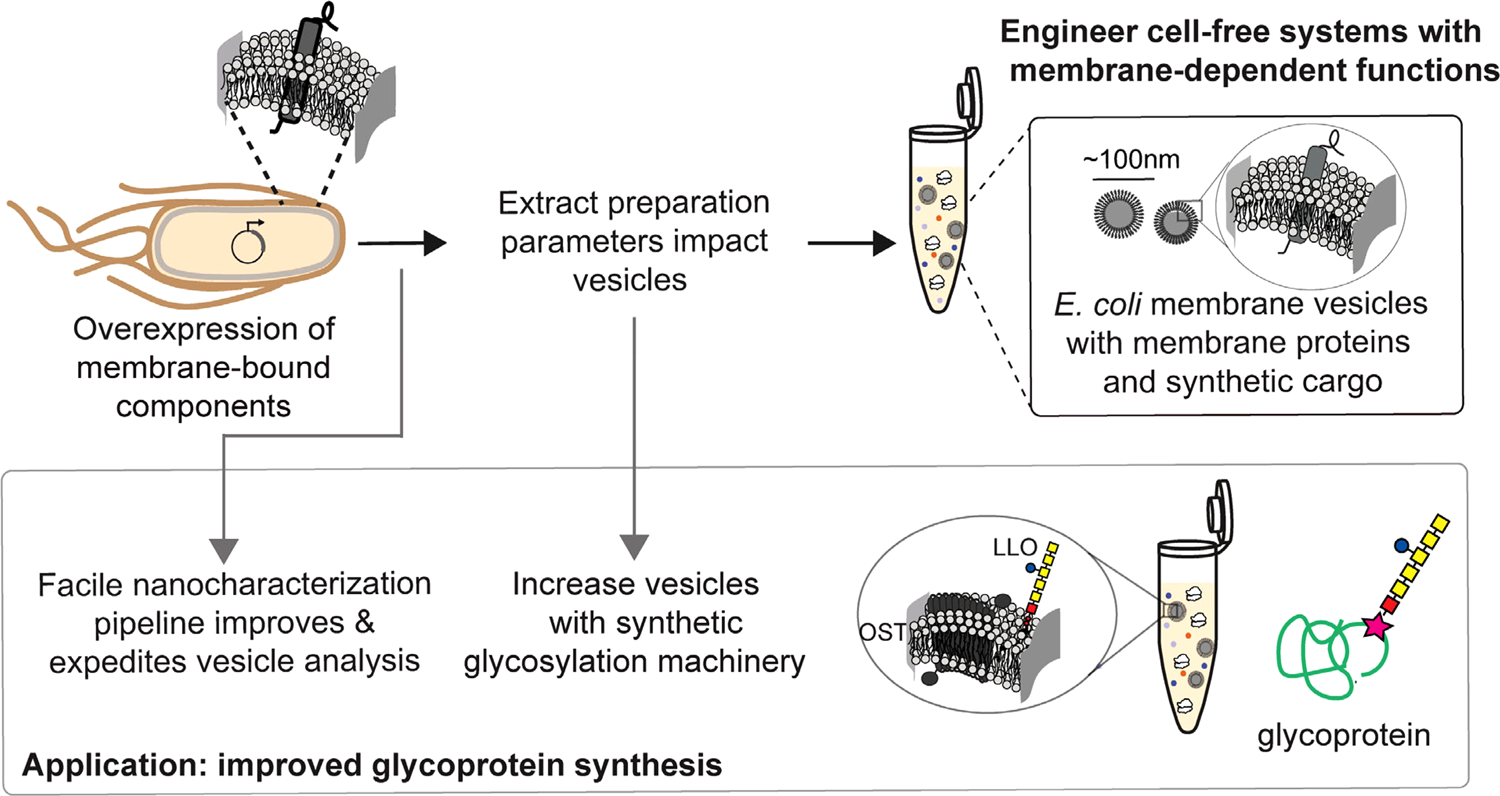
Improving cell-free glycoprotein synthesis by characterizing and enriching native membrane vesicles

Streptomyces cell-free systems for natural product discovery and engineering - ScienceDirect
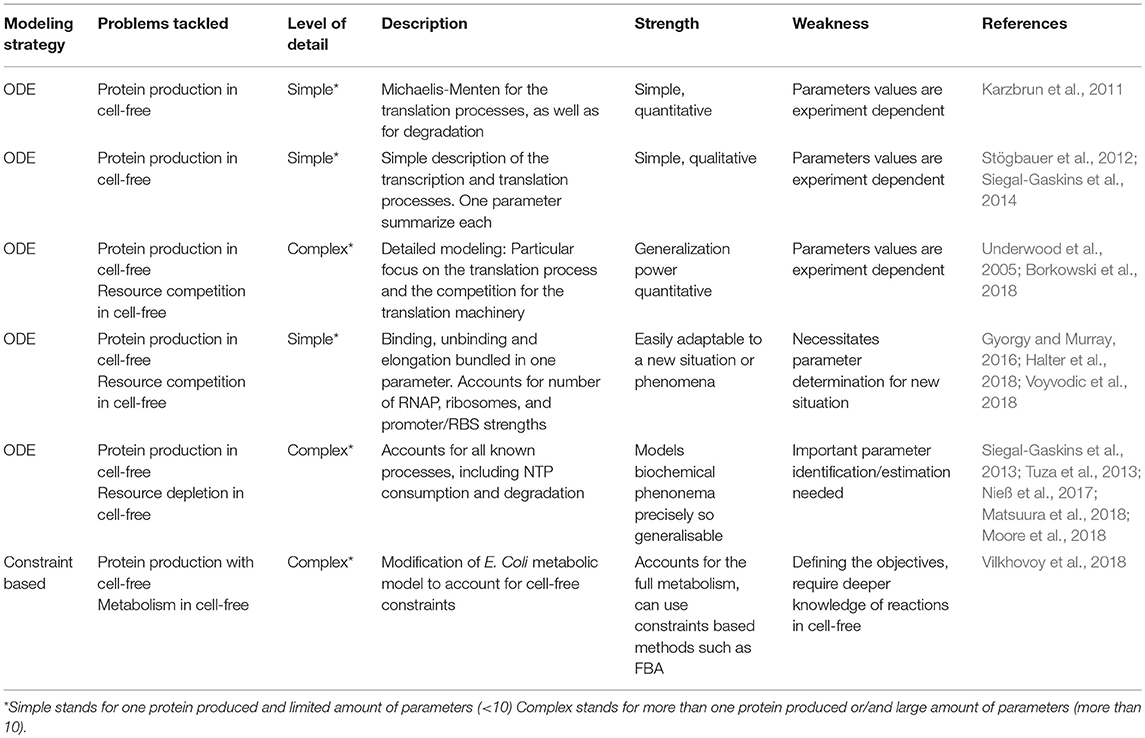
Frontiers Models for Cell-Free Synthetic Biology: Make Prototyping Easier, Better, and Faster
Full-spectrum cell-free RAN for 6G systems: s

Advances and applications of cell-free systems for metabolic production - ScienceDirect

Cell-Free Translation Systems

Cell-free mutant analysis combined with structure prediction of a lasso peptide biosynthetic protein B2
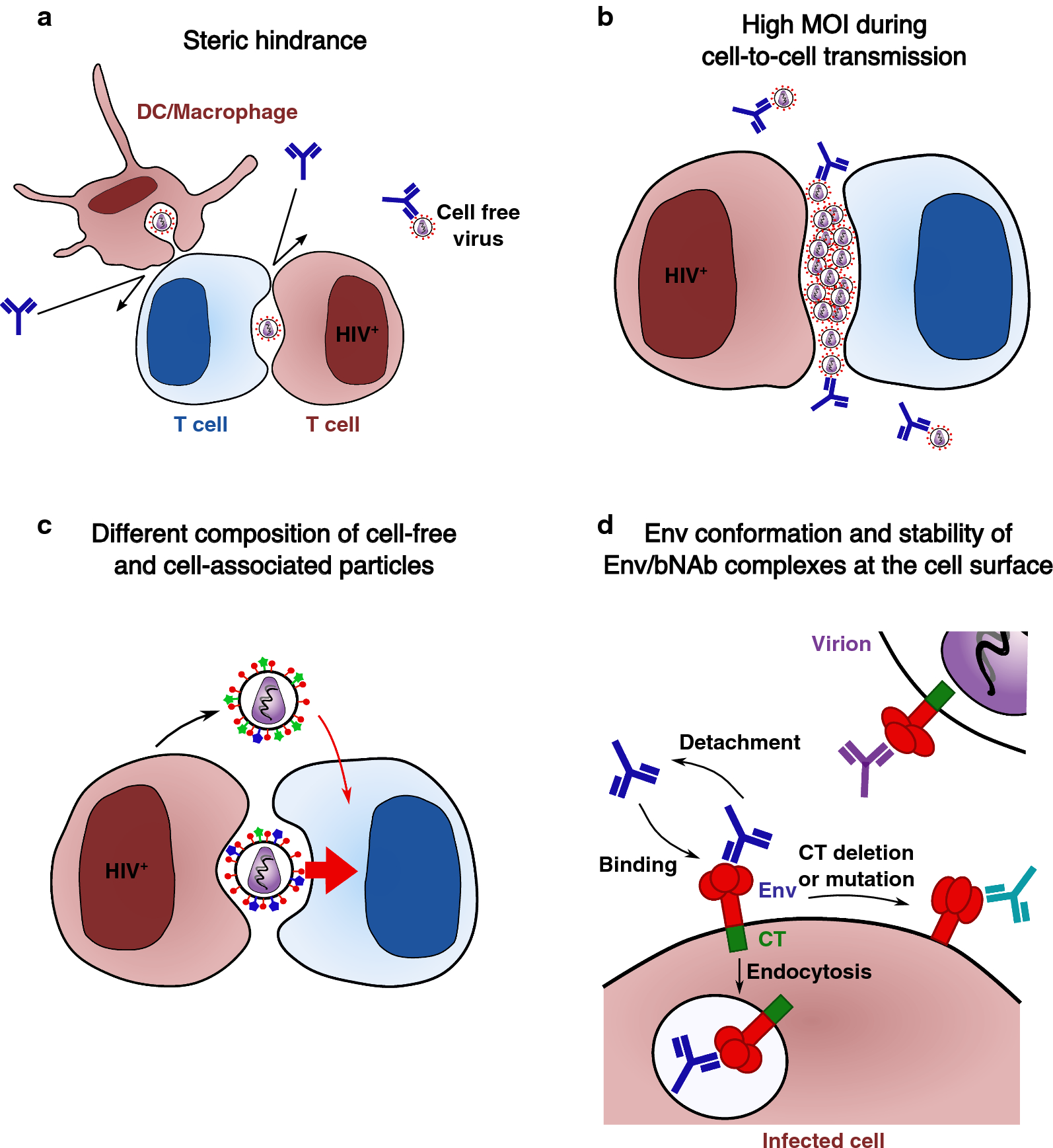
HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission and broadly neutralizing antibodies, Retrovirology
Recomendado para você
-
 Steel Spider Silk, TibiaWiki29 maio 2024
Steel Spider Silk, TibiaWiki29 maio 2024 -
 5 hours of crystal spiders later : r/TibiaMMO29 maio 2024
5 hours of crystal spiders later : r/TibiaMMO29 maio 2024 -
 Distribution of sizes at maturity (tibia–patella length = TPL) in29 maio 2024
Distribution of sizes at maturity (tibia–patella length = TPL) in29 maio 2024 -
 Spider anatomy - Wikipedia29 maio 2024
Spider anatomy - Wikipedia29 maio 2024 -
 Frozen Flowers Carpet – Tibia Fanart29 maio 2024
Frozen Flowers Carpet – Tibia Fanart29 maio 2024 -
 Everquest Live! - Guide - Farming Spider Silk29 maio 2024
Everquest Live! - Guide - Farming Spider Silk29 maio 2024 -
 Gotta bounce: Some spiders catapult away after sex to avoid death29 maio 2024
Gotta bounce: Some spiders catapult away after sex to avoid death29 maio 2024 -
![TUTORIAL] Giant Spider - Port Hope (Level 90+)](http://i.imgur.com/Fa1vTrL.jpg) TUTORIAL] Giant Spider - Port Hope (Level 90+)29 maio 2024
TUTORIAL] Giant Spider - Port Hope (Level 90+)29 maio 2024 -
![PDF] Sensory Biology of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/c483a4b9d330346831203eaa4dc3bd2a4e642881/3-Figure1-1.png) PDF] Sensory Biology of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi29 maio 2024
PDF] Sensory Biology of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi29 maio 2024 -
 Tibia MMORPG Sudden Death Rune SD T-Shirt tees blank t shirts anime mens graphic t-shirts big and tall - AliExpress29 maio 2024
Tibia MMORPG Sudden Death Rune SD T-Shirt tees blank t shirts anime mens graphic t-shirts big and tall - AliExpress29 maio 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Premium Photo Anime scenery wallpapers for your desktop, laptop29 maio 2024
Premium Photo Anime scenery wallpapers for your desktop, laptop29 maio 2024 -
 Hugo Weaving was supposed to be in The Matrix Resurrections29 maio 2024
Hugo Weaving was supposed to be in The Matrix Resurrections29 maio 2024 -
 Your.Local.Gacha Life.weirdo!~ Wallpapers - Page 2 - Wallpaper Cave29 maio 2024
Your.Local.Gacha Life.weirdo!~ Wallpapers - Page 2 - Wallpaper Cave29 maio 2024 -
 Basketball to the big screen: Former Gonzaga guard Jeremy Pargo to play lead role in self-written movie29 maio 2024
Basketball to the big screen: Former Gonzaga guard Jeremy Pargo to play lead role in self-written movie29 maio 2024 -
 p16-capcut-sign-va.ibyteimg.com/tos-maliva-v-be9c429 maio 2024
p16-capcut-sign-va.ibyteimg.com/tos-maliva-v-be9c429 maio 2024 -
Stray' — the videogame where you play as a cat — is breaking the internet - MarketWatch29 maio 2024
-
 Zoro One Piece GIF - Zoro One Piece Mocorongo - Discover & Share GIFs29 maio 2024
Zoro One Piece GIF - Zoro One Piece Mocorongo - Discover & Share GIFs29 maio 2024 -
 ChatGPT Prompts to Analyse Customer Feedback29 maio 2024
ChatGPT Prompts to Analyse Customer Feedback29 maio 2024 -
 majin vegeta ssj2 by Carlos3897983 on DeviantArt29 maio 2024
majin vegeta ssj2 by Carlos3897983 on DeviantArt29 maio 2024 -
![4k] Meguru Bachira Twixtor clips for editing (Blue lock) on Make a GIF](https://i.makeagif.com/media/5-01-2023/qKGhIh.gif) 4k] Meguru Bachira Twixtor clips for editing (Blue lock) on Make a GIF29 maio 2024
4k] Meguru Bachira Twixtor clips for editing (Blue lock) on Make a GIF29 maio 2024
